 |
Official Webpage |



ARM ENG |
|||||
|
|||||||
Astronomy in Iran routes back to many thousands years ago. When Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Persian Empire, captured Babylon in 539 B.C., magi who migrated there transformed Babylonian astronomy. They were the first to record planetary motion through constellations. In turn magi learned from the Babylonian astronomers as well and translated Babylonian books into the early Persian language. Andromeda galaxy was first identified by a Persian astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi calling it a little cloud in his book of fixed stars around 964. In 13th century, Maragheh Observatory with a unique place in the history of medieval astronomy, was established, representing a new wave of scientific activities in the Islamic world. It had a key role in the development of sophisticated pre-Copernican non-Ptolemaic systems for explaining the planetary motions, and it was the model for several observatories that were built in Persia, Transoxiana, and Asia Minor up to the 17th century.


IPM School of astronomy was established in early 2007 to facilitate the growth of observational astronomy and cosmology in a coherent fashion. Over the past few decades the perception of astronomical and cosmological research has been shifted to theoretical astrophysics and cosmology, a consequence of lack of investment in observational facilities and its related technology.
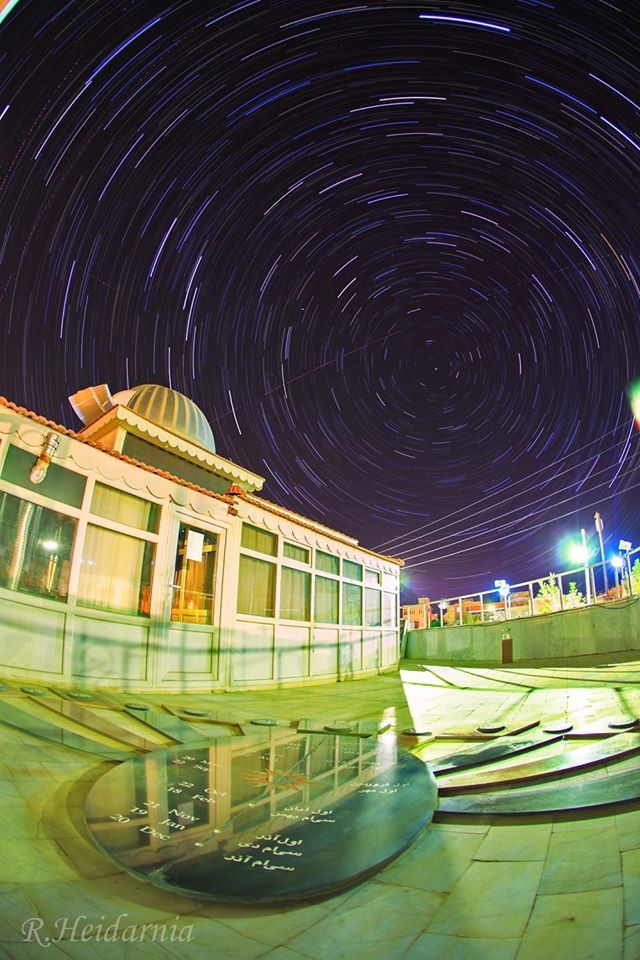

The RIAAM Observatory revivals and introduces the scientific and research will of Maragha’s Observatory. Besides, it shares itself in producing and introducing up-to-date science in astronomy and cosmology and doing research projects at international level. In this direction, the institute concentrates its main activity on developing research in the field of astronomy, astrophysics, cosmology and relevant technologies by designing plans which they are based on fundamental, development and applicative projects.
The Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS) is an advanced research center in Zanjan, Iran. It was founded in 1991.The goal of establishing IASBS was to provide a leading research-based institute in advanced science topics for both researchers and students in Iran.


The Ferdowsi University of Mashhad is a major comprehensive research university in Mashhad, capital city of the Iranian province of Razavi Khorasan. The university is named after Ferdowsi who is considered to be the national epic poet of Greater Iran, and was born in Tus, near Mashhad. It was established in 1949, making it the third oldest university in Iran.
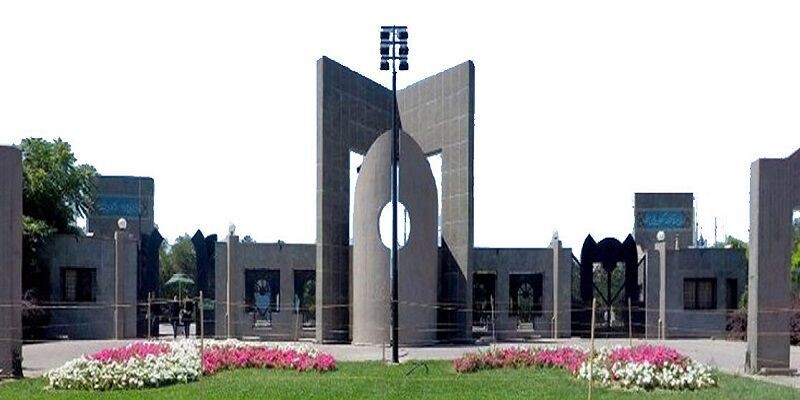

The Ferdowsi University of Mashhad strives to be one of the top universities in Iran in terms of scientific developments, developments in the theoretical and technological areas as well as maintaining its Iranian and Islamic identity.

The university tries to train creative, committed, and professional citizens and knowledgeable and capable researchers. The mission is accomplished when the Ferdowsi University of Mashhad can meet the needs of the society and maintain its cultural excellence by utilization of advanced technologies, compliance with international standards, and collaboration with scientific and cultural centers. The Ferdowsi University of Mashhad tries to advance the frontiers of knowledge both nationally and internationally.
The University of Tabriz is a public university located in Tabriz, East Azarbaijan with the fundamental aim of creating a center of excellence in higher education and research.

The University of Tabriz is the second-oldest university in Iran after the University of Tehran, and has the second largest campus area in the country which is the biggest academic institution in northwest of the country. The university is also a member of the Caucasus University Association.
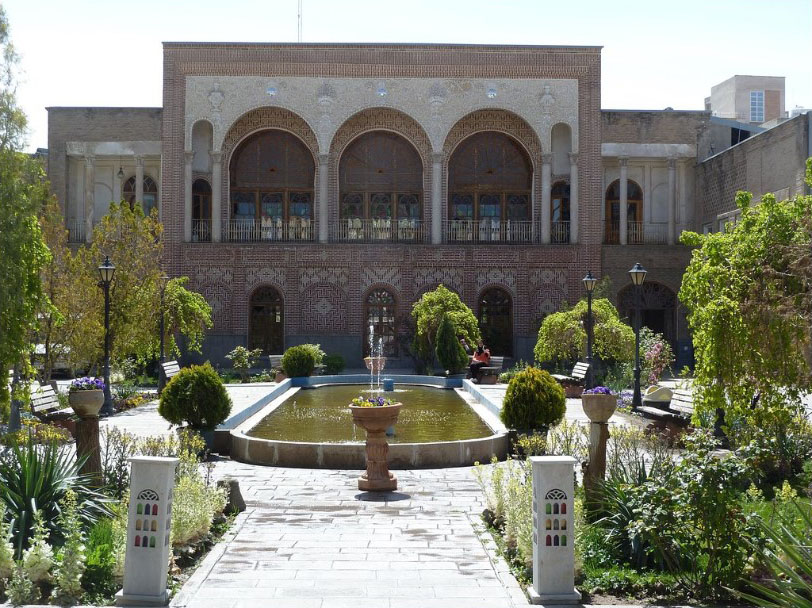
Shiraz University, formerly known as Pahlavi University, is a public university located in Shiraz, Iran. It is both a modern as well as old institution of Higher Education in Iran. Established in 1946, the University has, since then, applied itself to the advancement of knowledge no less than to its dissemination.

Shiraz University, formerly known as Pahlavi University, is a public university located in Shiraz, Iran. It is one of the major universities of Iran. Shiraz University has always ranked as Top 5 among Iranian universities and is well respected in Iran.
The University of Birjand is the largest and oldest public university in the east of Iran. It was founded in 1975. Currently, the University of Birjand includes 14 faculties and colleges. It is now home to more than 12000 students studying in more than 330 graduate and undergraduate programs with more than 360 full time and many other part-time faculty members.

The university strives to extend and localize modern knowledge and technologies and educate creative and committed experts who consider local, national, and international needs and address the national and international challenges to reach sustainable development.
Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman (SBUK) is a research institution and university of engineering and science in Iran, offering both undergraduate and postgraduate studies. Located in Kerman province of Iran, the university is among the top ten universities and research institutes in Iran, illustrating its high status in research and education.
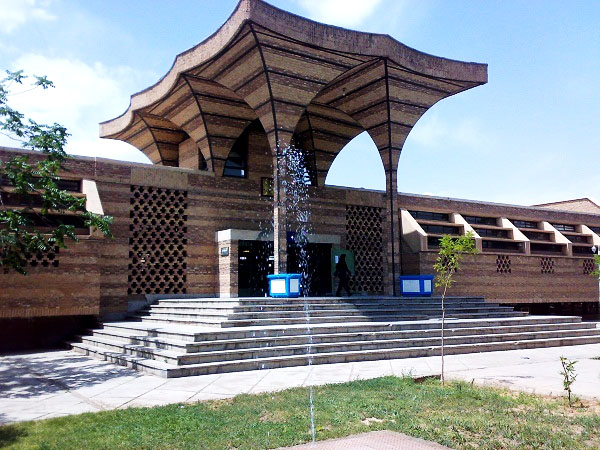

The Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman features several Libraries. There is one main library and also each college has a separate library of its own. The main library of the university is called the Central Library and Documentation Center.
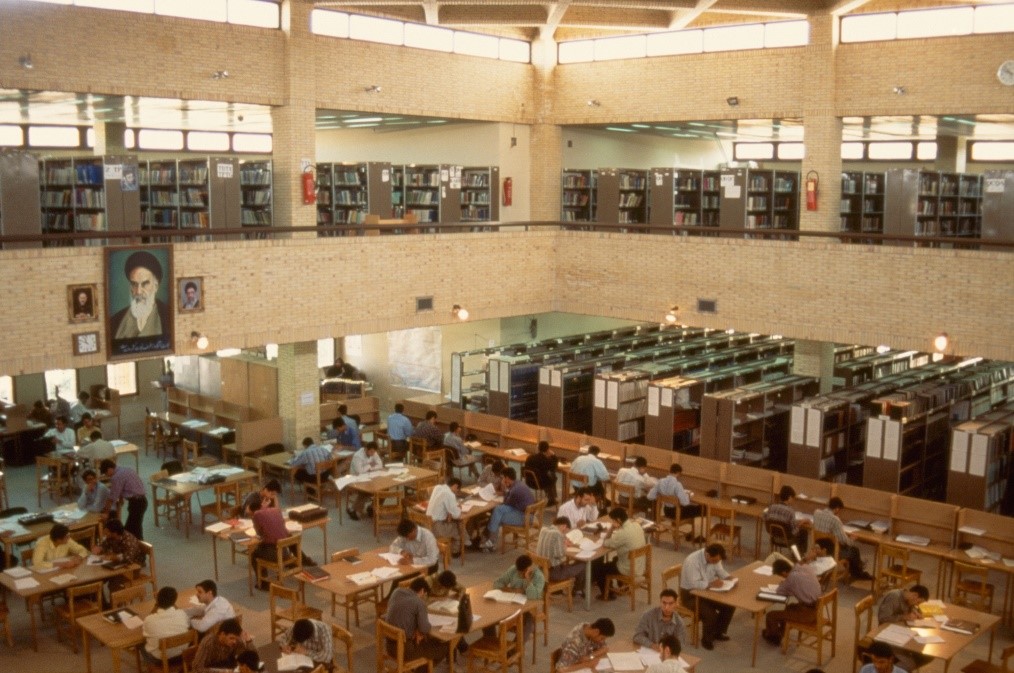

University of Zanjan (the Ex Higher School for Agriculture & Animal Science) started its activities in 1975, on a formal basis. In December 1975, as ratified by the state council a land (with an area of 400 hectares) was dedicated by the Forestry Organization to University of Zanjan for the purpose of educational as well as developmental and physical activities. On Feb 20, 1976 Zanjan higher school for Agriculture & Animal Science started its work under new title Zanjan Agriculture & Animal Science College while it enhanced its Agriculture & Animal Science Courses to a BS. Level.

Nowadays it is one the largest universities of the country with a community of over 10,000 students. At the 2006 census, population of the nearby urban area (Zanjan city which is about 5 km away) was over 400s and the nearby rural area was only 125.
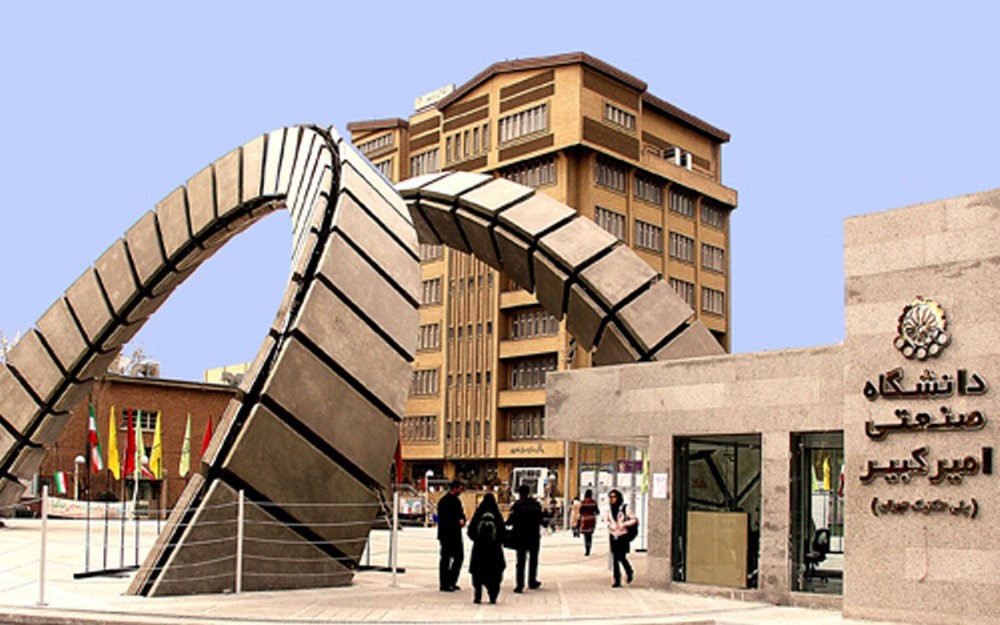

Sharif University of Technology (SUT), is a public research university in Tehran, Iran and is widely considered to be the nation's leading institution for engineering and physical science disciplines. The international campus of the university is located in Kish Island, Persian Gulf.
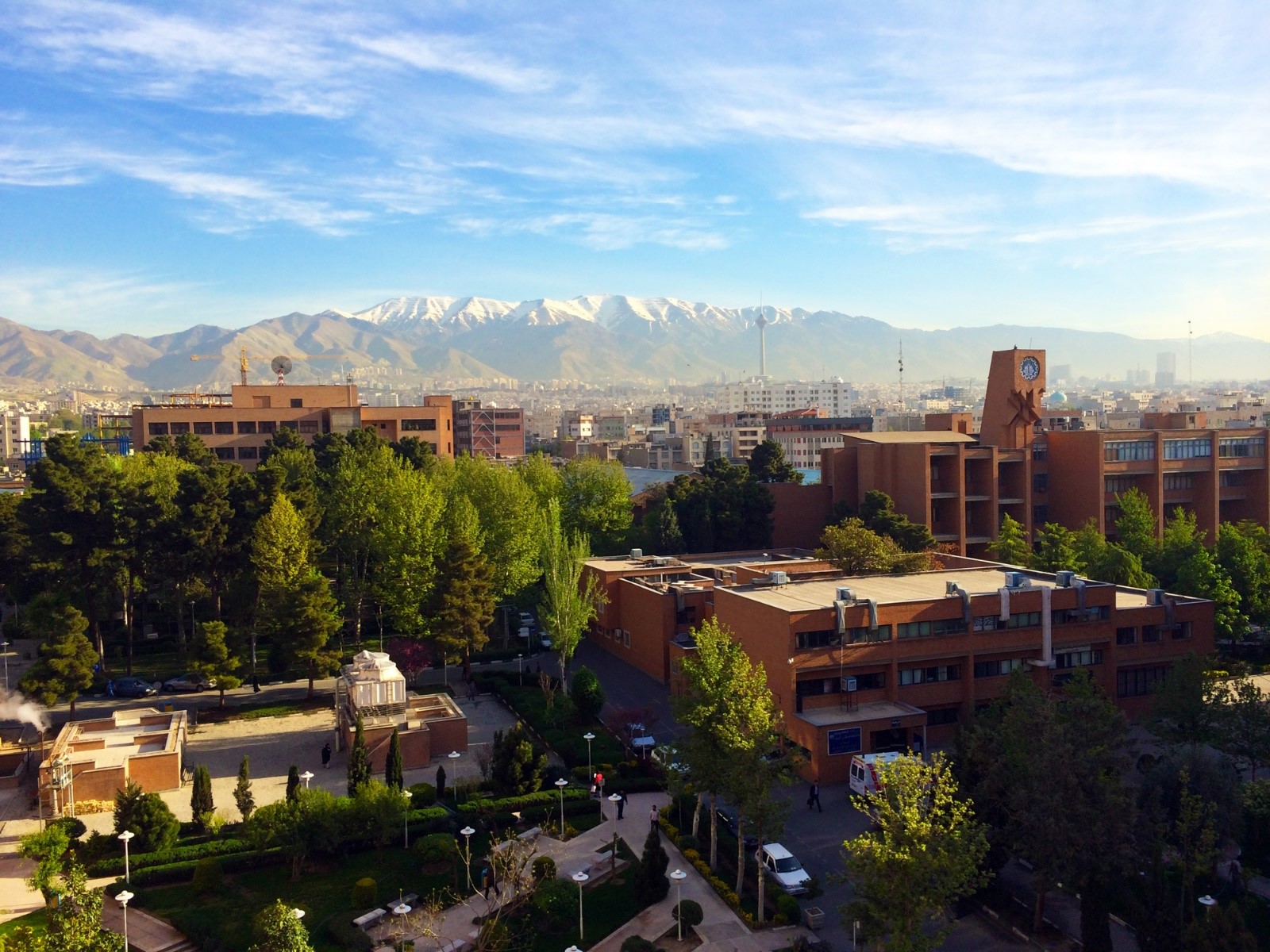

The main campus of the university is located in the Tarasht neighborhood, near Azadi Square, Tehran, Iran. It is located close to the Azadi Tower, which is the symbol of Tehran and one of the main transportation hubs. The endowment of Sharif University of Technology has been estimated at around $25 million.
Maragheh observatory was an astronomical observatory established in 1259 CE under the patronage of the Ilkhanid Hulagu and the directorship of Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, a Persian scientist and astronomer. Located in the heights west of Maragheh, which is today situated in the East Azerbaijan Province of Iran, it was once considered "the most advanced scientific institution in the Eurasian world".
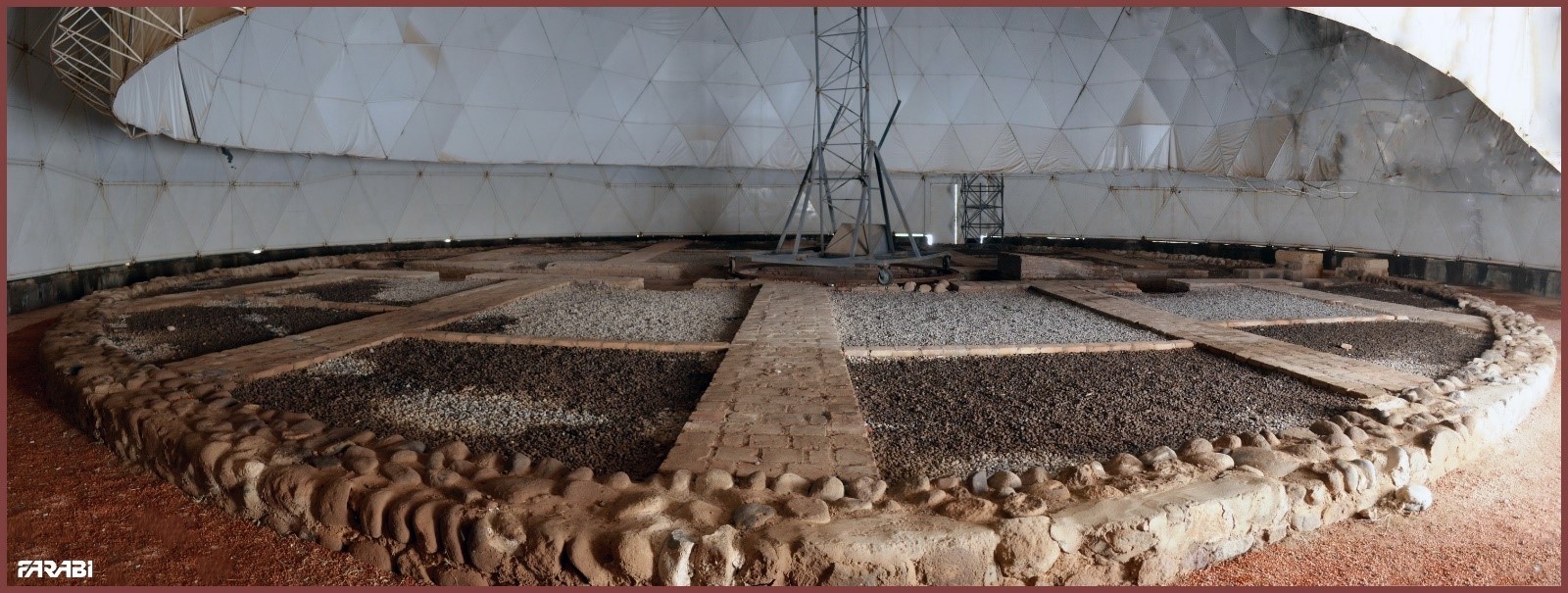

After 1978, Tabriz University, which is located near the observatory, was placed in charge of its preservation. Today the site is home to occasional star parties and, though there are no official tours offered, the public is still welcome to come and see the remains of the observatory.
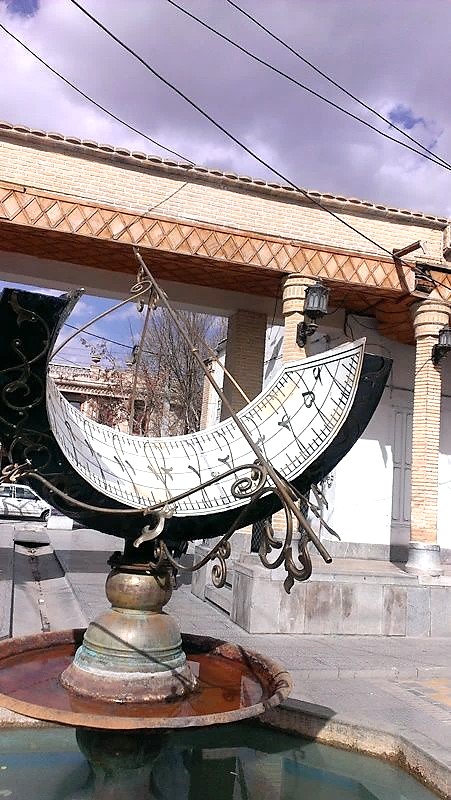
Designing sundials has a long history in Iran. In an astronomical book entitled Zij-e Shahriyar ("Astronomical tables of the King"), composed in pre-Islamic Iran possibly in 555 C.E., there was a chapter on a method for graduating sundials.

Jameh Mosque of Qazvin is one of the oldest mosques in Iran. The oldest part of the mosque is said to have been constructed by the orders of Harun al-Rashid in 807CE. The foundation of the mosque is laid on a Zoroastrian fire temple.

The Fire Temple of Yazd, is a Zoroastrian fire temple in Yazd. It enshrines the Atash Bahram, meaning “Victorious Fire”, dated to 470 AD. The highest grade of fire temples were first constructed in the Sasanian Empire for the reverence of fire, which is the manifestation of Ahura Mazda in the Zoroastrian religion. Zoroastrian prayers are to be said in the presence of light, either in the form of fire or the sun.

A bust of Manekji Limji Hataria, who was instrumental in raising funds for building the temple, has been installed in the precincts of the temple. The bust also displays the Zoroastrian divine symbols of the Sun and the Moon.
The ruins of many temples belonging to Sassanid dynasty have been found in different parts of Iran especially in Fars, and Kerman provinces. It is interesting to know that during Sassanid dynasty, there were three highly significant fire temples in Iran: Azar Goshnasb, Azar Barzin Mehr or Azar Borzin Mehr, and Azar Faranbagh.

Each of the fire temples belonged to a special society class and it was believed that Ohrmazd had created the three of them for protection of the world. The fire temple of Azar Goshnasb belonged to kings and armies, the fire temple of Azar Franbagh belonged to the priests, and the fire temple of Azar Borzin Mehr belonged to the farmers.